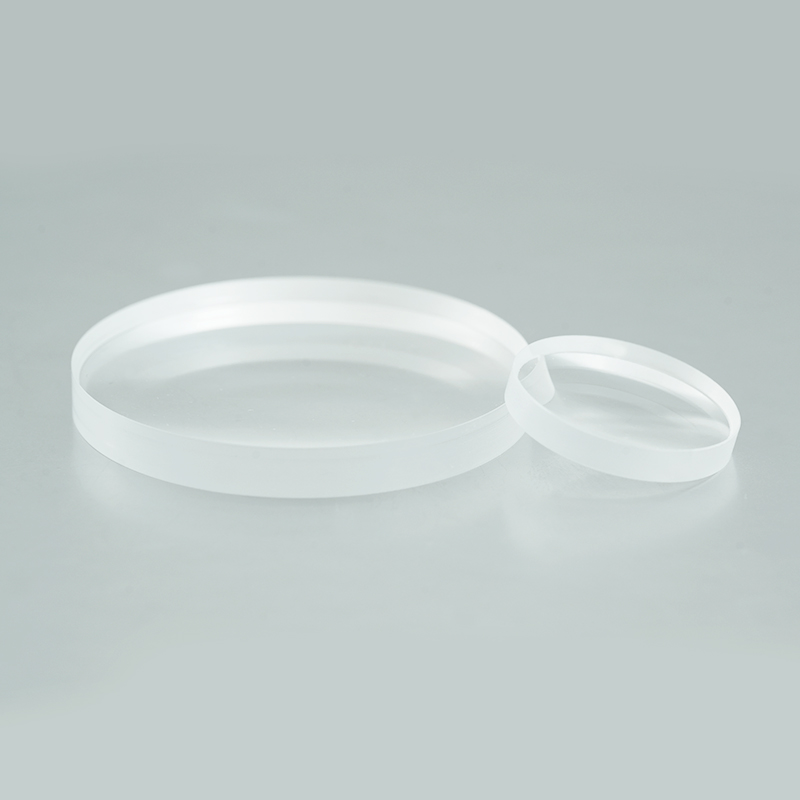
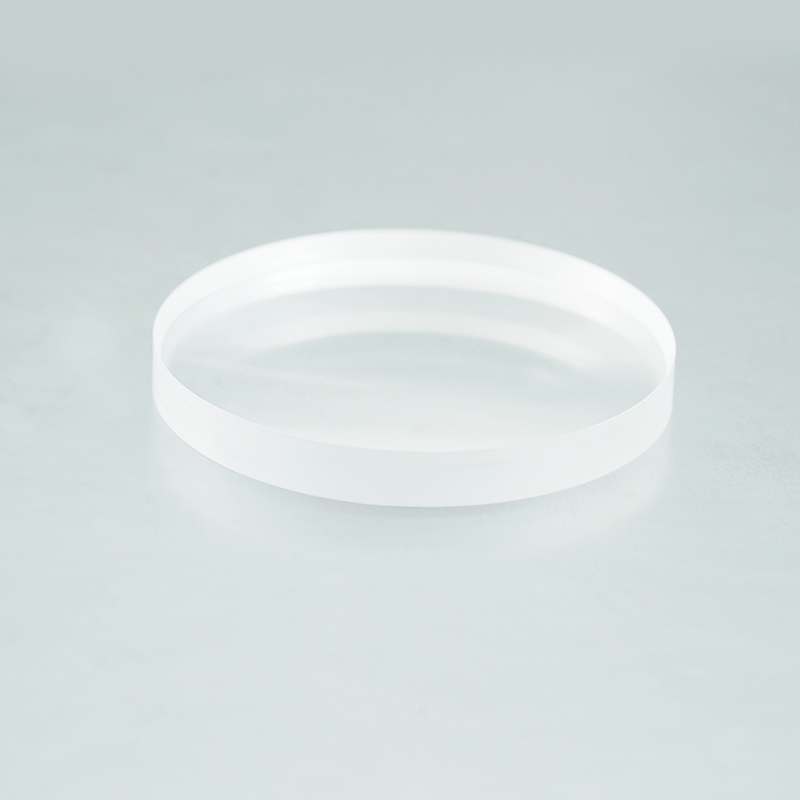
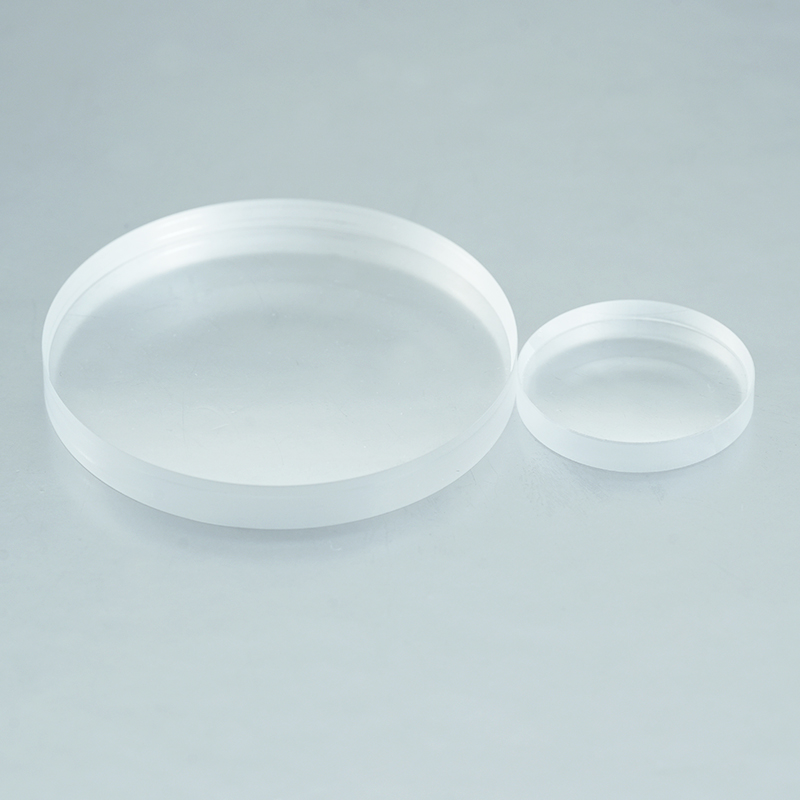
N-BK7 Plano-Concave Lenses
Product Introduction:
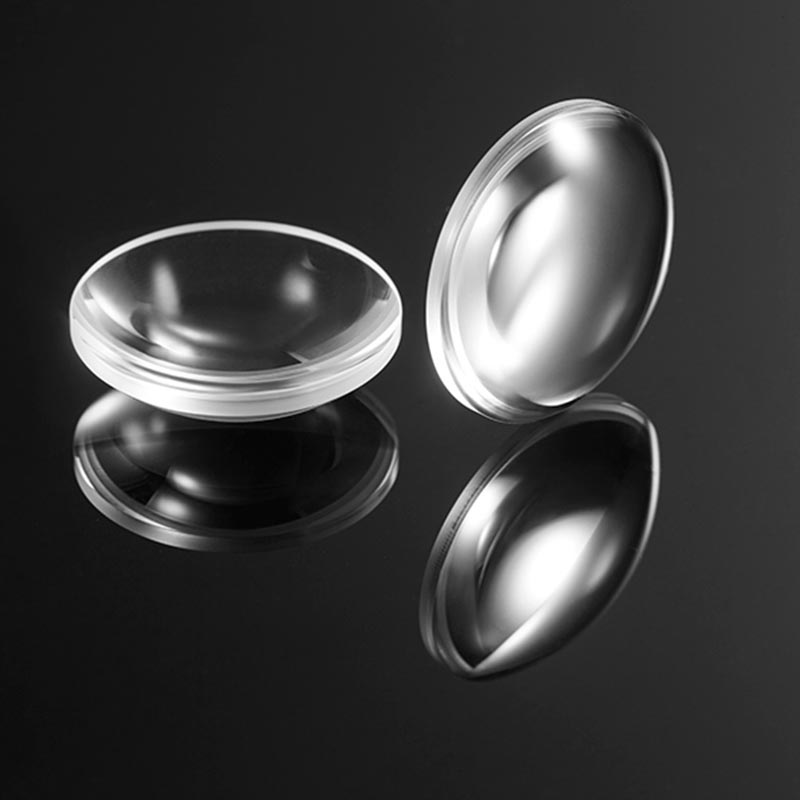
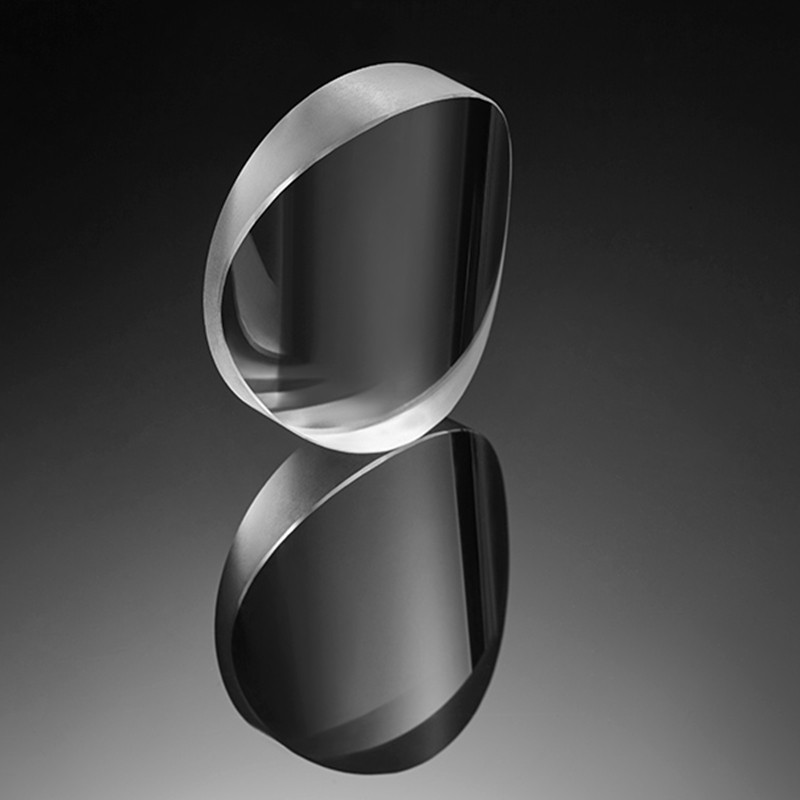
The plano-concave lens is composed of a flat surface and a concave spherical surface, which can produce negative spherical aberration and is often used in systems where the light is expanded or the focal length is increased to balance the deviation of other lenses.
N-BK7 is widely used in a variety of visible and short-wave infrared applications, and its advantages over other similar glasses are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
high performance, low cost, good material consistency, high homogeneity of refractive index, low stress birefringence, low bubbles and streakiness.
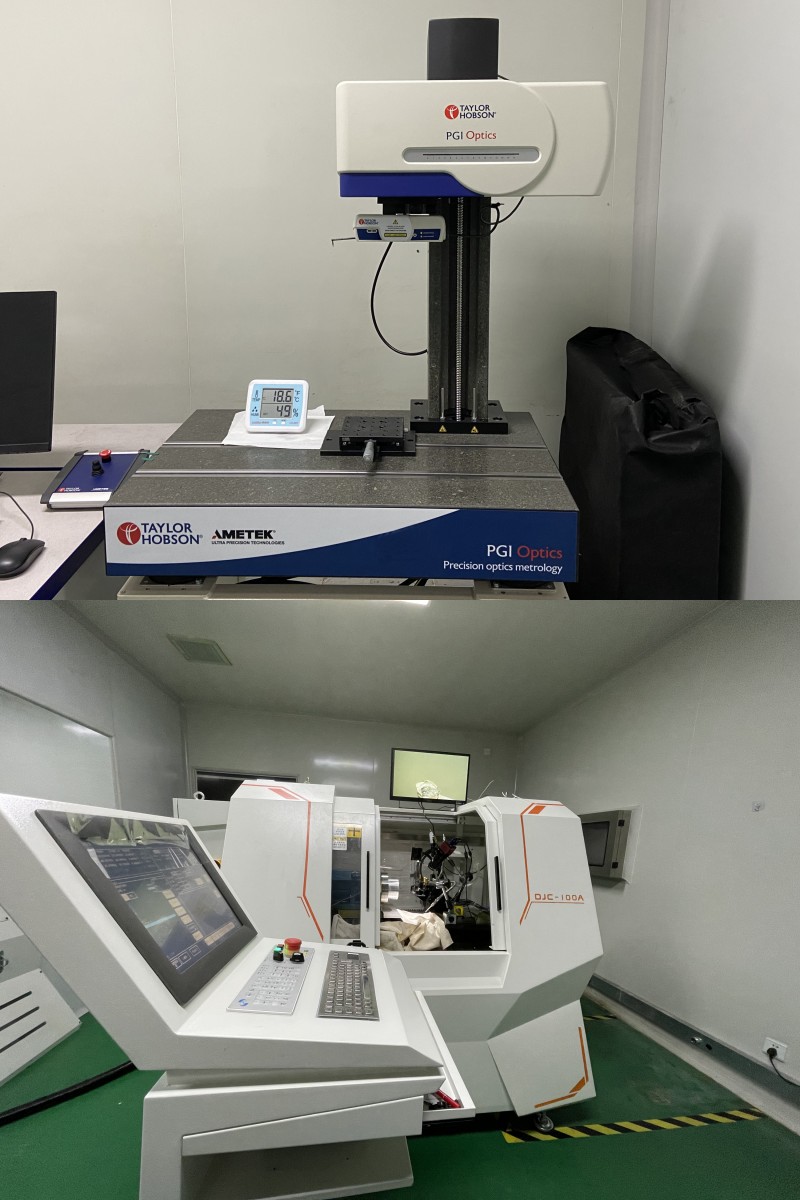
Our Company can provide calcium fluoride (N-BK7) plano-convex lenses with diameters from 2-300mm and thicknesses from 0.12-60mm (accuracy up to 20-10, 1/10L@633nm), with 4 major processes: gel disc polishing, high speed polishing, ring polishing and CNC polishing, with ZYGO, AFM, reflection and transmission eccentric meters, 15 second goniometer, UV gel centering system, non-contact Laser. Thickness gauge, 2D imager and sphere diameter gauge to ensure the accuracy of data.
Coating selection:
MgF2,UV-AR,UV-VIS ,VIS-EXT, VIS-NIR, NIR I, NIR II, Telecom-NIR,SWIR ,SWIR ,YAG-BBAR.

The N-BK7 is widely used in a variety of visible and short-wave infrared applications.The N-BK7 plano- concave lenses disperses a collimated beam from a virtual focal point and is commonly used in Galileo-type beam expanders.
Our company offer N-BK7 plano-concave lenses in various sizes and focal lengths.
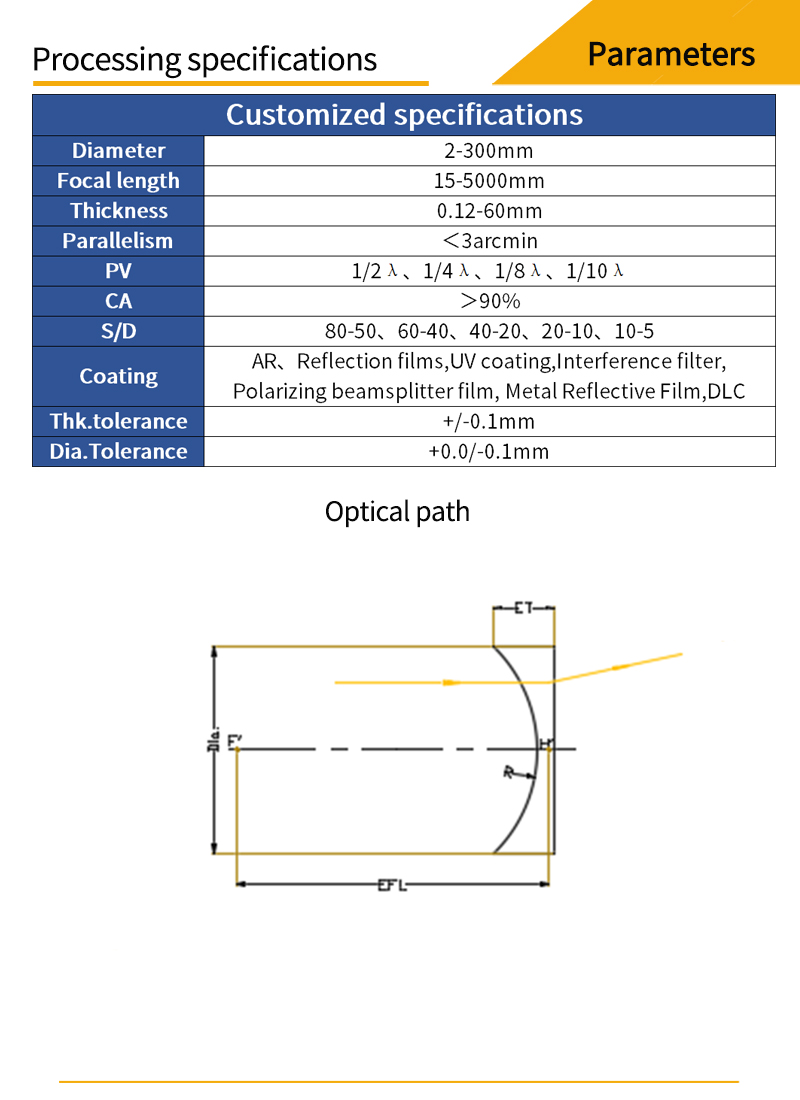
Plano-concave lens with one concave side and one flat side can spread the light out and has a negative focal length.Plano-concave lenses are often used for beam extension, projection and focal length expansion of optical systems.The plano-concave lenses has a negative focal length and negative spherical aberration, which can be used to offset the aberration of other lenses in the system. To obtain a smaller spherical aberration, the collimated beam should be incident on the concave side of the plano-concave lenses when the incident beam is collimated.
The important parameters of a plano-concave lens are: size, focal length, design wavelength, finish, face accuracy, eccentricity, substrate material and other attributes. Suitable parameters of plano-concave lenses can be selected according to specific applications.

Material Description
N-BK7 is widely used in a variety of visible and short-wave infrared applications, and its advantages over other similar glasses are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
●High performance and low cost.
●Good material uniformity .
●High homogeneity of refractive index.
●Low stress birefringence .
●Low bubbles and streakiness.
Material characteristics
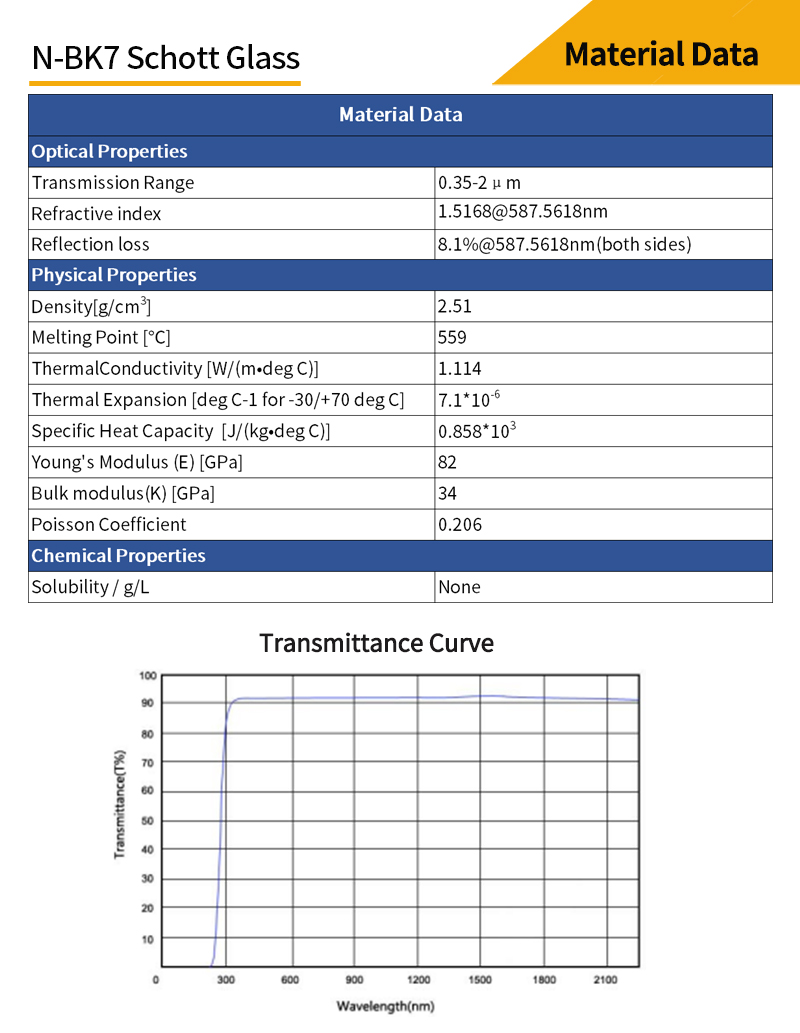
The high quality of optical materials is reflected in their homogeneity and, more specifically, in the extremely narrow range of refractive index variation of the entire glass. Therefore, optical glasses for high-power lasers and astronomical applications in particular require extremely high homogeneity. N-BK7 can withstand low transition temperatures, mostly below 550°C, which improves mold life and reduces press time.
● Low chemical reaction tendency with mold material in the molding temperature range.
●Strict optical tolerances .
●A wide range of glass sizes are available.
●A wide range of supply options for optical raw materials, optical blanks, optical parts, etc. .
Applications
● High-energy laser technology, measurement technology.
● industry .
●Satellite technology, imaging applications in astronomical applications.
N-BK7 has many advantages, such as high performance, low cost, good material consistency, high homogeneity of refractive index, low stress birefringence, and low bubbles and streakiness

Coating refers to coating a transparent electrolyte film or metal film on the surface of the substrate material by physical or chemical methods. The purpose is to change the reflection and transmission characteristics of the material surface to reduce or increase the reflection, beam splitting, color separation, light filtering, polarization and other requirements.We can provide various optical coatings such as anti-reflective films, high-reflective films, spectral films, and metallic films. Broadband anti-reflective films are available for UV, visible, NIR and mid-infrared wavelengths.

●N-BK7
N-BK7 is the most commonly used optical glass for processing high quality optical components,, with excellent transmittance from visible to near-infrared wavelengths(350-2000nm), and has a wide range of applications in telescopes, lasers and other fields. N-BK7 is generally chosen when the additional benefits of UV fused silica (very good transmittance and low coefficient of thermal expansion in the UV band) are not required.
●UV fused silica
UV fused silica has a high transmission from the UV to NIR (185-2100nm). In addition, UV fused silica has better uniformity and lower coefficient of thermal expansion than H-K9L (N-BK7), making it particularly suitable for high power laser and imaging applications.
●Calcium fluoride
Due to its high transmittance and low refractive index within a wavelength of 180nm-8um, calcium fluoride is often used as windows and lenses in spectrometers and thermal imaging systems. In addition, it has good applications in lasers because of its high laser damage threshold.
●Barium fluoride
Barium fluoride have high transmittance from the 200nm-11um and they are resistant to stronger high-energy radiation. At the same time, barium fluoride has excellent scintillation properties and can be made into various infrared and ultraviolet optical components. However, the disadvantage of barium fluoride is that it is less resistant to water. When exposed to water, the performance degrades significantly at 500℃, but it can be used for applications up to 800℃ in a dry environment. At the same time, barium fluoride has excellent scintillation properties and can be made into various infrared and ultraviolet optical components.It should be noted that when handling barium fluoride material, gloves must be worn at all times and hands must be washed thoroughly after handling.
●Magnesium fluoride
Magnesium fluoride is ideal for applications in the wavelength range of 200nm-6um. Compared to other materials, magnesium fluoride is particularly durable in the deep UV and far IR wavelength ranges. Magnesium fluoride is a powerful material for resistance to chemical corrosion, laser damage, mechanical shock and thermal shock. It is harder than calcium fluoride crystals, but relatively soft compared to fused silica, and has a slight hydrolysis. It has a Nucleus hardness of 415 and a refractive index of 1.38.
●Zinc selenide
Zinc selenide has high transmittance in the 600nm-16um and is commonly used in thermal imaging, infrared imaging, and medical systems. Also, due to its low absorption, zinc selenide is particularly suitable for use in high-power CO2 lasers. It should be noted that zinc selenide is a relatively soft material (Nucleus hardness 120) and is easily scratched, so it is not recommended for use in harsh environments. Extra care should be taken when holding, and cleaning, pinching or wiping with even force, and it is best to wear gloves or rubber finger covers to prevent tarnishing. Cannot be held with tweezers or other tools.
●Silicon
Silicon is suitable for use in the NIR band from 1.2-8um.Because of its low
density, silicon is particularly suitable in applications where weight
requirements are sensitive, especially in the 3-5um . Silicon has a Nucleus
hardness of 1150, which is harder than germanium and not as fragile as
germanium.It is not suitable for transmission applications in CO2 lasers
because of its strong absorption band at 9um.
●Germanium
Germanium is suitable for use in the near-infrared band of 2-16um and is well
suited for infrared lasers. Due to its high refractive index, minimal surface
curvature and low chromatic aberration, germanium does not usually require
correction in low power imaging systems. However, germanium is more
severely affected by temperature, and the transmittance decreases with
increasing temperature; therefore, it can only be applied below 100°C. The
density of germanium (5.33 g/cm³) is taken into account when designing
systems with strict weight requirements. Germanium lenses feature a
precision diamond lathe turned surface, a feature that makes them well suited
for a variety of infrared applications, including thermal imaging systems,
infrared beam splitters, telemetry, and in the forward-looking infrared (FLIR)
field.
●CVD ZnS
CVD ZnS is the only infrared optical material, other than diamond, that covers visible to long-wave infrared (LWIR), full wavelength and even microwave wavelengths, and is currently the most important LWIR window material. It can be used as windows and lenses for high-resolution thermal imaging systems, as well as for advanced applications such as "tri-optical" windows and near-infrared laser/dual-color infrared composite windows.